RMalloc
RMalloc is a malloc implementation which means, a dynamic memory allocator .
One reason for this version of malloc was a problem I encountered with one of my other programs when allocating several gigabytes. Because of the used algorithms I deallocated and allocated most of this memory (which was used by relativly small chunks). This behaviour confused all other malloc implementations I tested and led to unacceptable program-performance. So I decided to do it by myself and wrote this lib which performed MUCH better.
The first version was a simple segregated storage allocator without splitting and coalescing. Allthough it was much faster and scaled very well wrt. the number of processors, it suffered from severe fragmentation (as is known for such kind of allocators) when used with a special variant of one of my other projects (see libHmatrix). But it performs very well if the application only uses a limited number of different sizes when allocating blocks.
To reduce this fragmentation I completly rewrote the allocator and added splitting and coalescing. It now works similar to LKmalloc by using private heaps with ownership for each threads. Thereby each memory-chunk is put back into the heap, it was allocated from.
The main differences between rmalloc and LKmalloc are the handling of small blocks, the allocation of memory from the operating system and the mapping of heaps to threads.
For performance reasons small chunk are only allocated from containers, which hold several equal sized chunks. Especially if a lot of small blocks are allocated, this improves the overall performance of the allocator. This also avoids splitting and coalescing these small blocks (which might reduce fragmentation).
Memory from the operating system is not allocated in equal sized stripes (as in LKmalloc) but in dynamically growing chunks via mmap (or sbrk). This reduces the number of calls to these system-functions. The size of each chunk is adjusted according to the memory in use.
Heaps are associated to threads by using thread-private data (via PThread-functions). Thereby the number of heaps is automatically adjusted to the number of concurrent threads (LKmalloc need some initialisation for this).
Quelltext
RMalloc is free software where free is defined by the GNU Lesser General Public License. So share and enjoy ;).
ChangeLog
v1.1
- implemented deallocation of empty data segments if enough free memory is available
- non-empty wilderness are now handled by middle-sized management ensuring good-fit allocation on wilderness (greatly reduces internal fragmentation in certain situations)
- support for 16 byte alignment added (for SSE applications)
- fixed bug when setting size of split blocks
- modified message and error output
- changed Rmalloc tracing to write more data
- removed STAT_FRAGMENTATION (was not used anymore)
- guarded munmap by mutex in mt-mode (seems to be not mt-safe)
- non-handled (large) blocks are now part of statistics
v1.0.3
- changed license to LGPL
- ported to Win32
- guarded special functions by defines (mmap, getpagesize, etc.)
- moved trace.fd to trace.file (file IO instead of read/write)
- C++ operators now really throw std::bad_alloc
v1.0.2
- handling of NULL pointers in allocation improved; no more ABORT but NULL-returns
v1.0.1
- in check_rmalloc: global heap was not checked
- consistency check of wilderness, full/non-empty containers
- alignment of size for heap-allocation
v1.0
- removed bug in
r_realloc(wrong size for given block)
v1.0-pre5
- NO_OF_CLASSES, NO_OF_SMALL must be even; changed
v1.0-pre4
- reduced internal fragmentation for small chunks by using a special type (sblock_t)
- minor bugfixes for non-pthread mode
v1.0-pre3
- added USE_THR_HACKS to simulate thread-specific-data
- restructured container-management; the empty-list not needed anymore
v1.0-pre2
- removed needless data-segment-structure
- removed needless empty-lists for containers
v1.0-pre1
- another major rewrite: added coalescing similar to LKmalloc
- maintained container-managment for small blocks and coalescing strategy for middle sized blocks
- removed rounding up of size-requests
- no longer memory-transfers between heaps
v0.99
- major rewrite with containers which can be reused by other size-classes ⇒ led to massive fragmentation
v0.98.3
- various code-cleanups
- removed size-class generation (now in extra file)
v0.98.2
- replaced “real” thread-private-data by simulated one
v0.98.1
- active fragmentation statistics with STAT_FRAGMENTATION (prints “real” consumption)
- moved top_pad into data-segment-structure
v0.98
- used remaining blocks of each data-segment to serve future requests, thereby reducing fragmentation (left-over-blocks)
v0.97
- small bugfixes
- top_pad is now heap-specific and adjusted dynamicly (1/TOP_PAD_FRACTION of mem_used)
- changed size-field in nodes to slot; avoided to many calls to size_to_class
- moved handling of sizes larger than biggest size-class to operating-system (via malloc or mmap)
- fixed error-handling if no memory is available from the OS (sends kill to own process instead of exit(1))
- added another trace-method: trace by allocation
v0.96
- rewritten chunk-handling: heap -> block -> chunk
- exchange of blocks between thread-heaps and global-heaps to reduce overall memory-consumption
v0.95
- round sizes to next size-class to guarantee, that there is a free chunk in the list (avoid searching)
- increased number of size-classes; changed size_to_class to use a binary search instead of linear
- ok. maybe 10 MB for the DEFAULT_TOP_PAD is better ?
- implemented trace-functionality for thread-heaps
v0.94
- rearranged code for system-allocation (mmap and malloc had too much in common to be separated)
- removed most messages when mutices were locked
- set MMAP to be default, even when malloc is not overwritten
- changed “r_mallinfo” to “rmallinfo” and added declaration in rmalloc.h
v0.93
- changed heap handling, now each thread has a private heap; if the thread terminates, this heap is then marked as free and can be used by a new thread
- removed creation of first heap (besides global-heap), this will now be done on demand (in r_malloc)
- DEFAULT_TOP_PAD reduced to 5 MB (should also be enough)
- heap-list is no longer a circular list (just a linear one)
- heaps can now be aligned to the cache-line-size (ALIGN_TO_CACHE_SIZE); off by default
- added wrapper for mallinfo which calls internal r_mallinfo (r_mallinfo uses mallinfo-struct with ulong fields)
v0.92
- replaced simulated thread-specific-data by real one
v0.91
- fixed bug/feature when using malloc as system-alloc: only requested chunks of needed size were allocated, not plus DEFAULT_TOP_PAD
v0.90
- initial public release
Benchmarks
These benchmarks are similar to the benchmarks used to show the properties of hoard.
ThreadBench-Eq
This benchmark allocates a lot of small, equal sized chunks in each thread and tests the parallel efficiency.
The following table shows the time for the different allocators when running sequentially.
| Sun-malloc | MT-malloc | Hoard | PTmalloc | Rmalloc |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 132.2 sec | 219.7 sec | 131.7 sec | 119.8 sec | 115.7 sec |
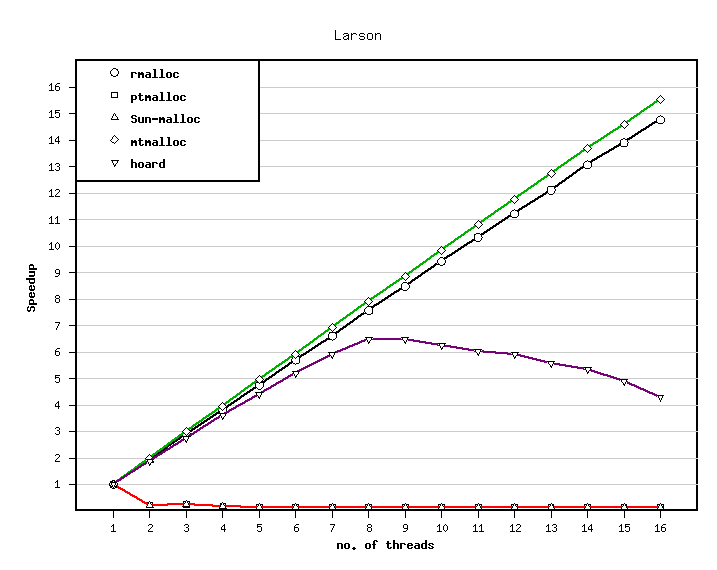
The speedup wrt. the number of processors is shown in the following figure.
Larson
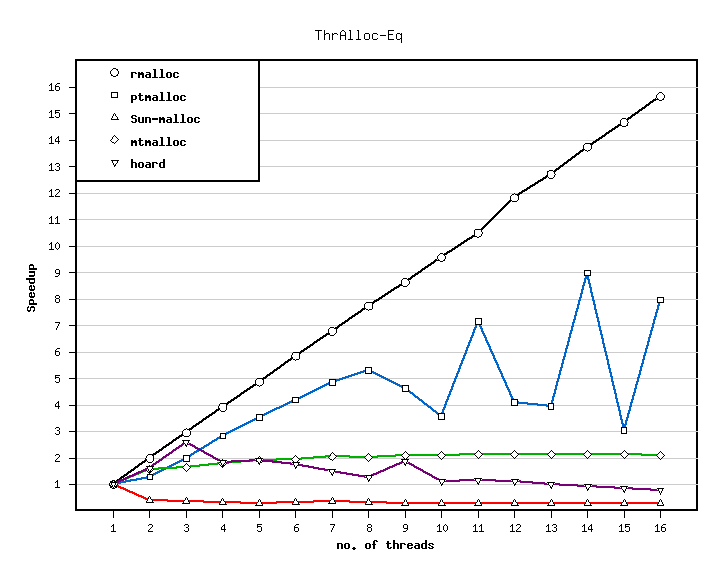
This benchmarks simulates the allocation behaviour of a typical server application with multiple threads.
The number of allocations per time on one processor is shown in the following table.
| Sun-malloc | MT-malloc | Hoard | PTmalloc | Rmalloc |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 579345 | 580463 | 622875 | 577604 | 753322 |
The speedup of the different allocators is shown in the next figure.